- Dynamic Programming Ppt
- Introduction To Computer Programming Ppt
- Control Statements In C Programming Ppt
- C++ Basics
- C++ Object Oriented
- C++ Advanced
- C++ Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
- Control Structures: 6. Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose, C provides control structures that serve to specify what has to be done by our program, when and under which circumstances.
- Here we discuss the different types of Control Statements in C like If, Switch, Conditional Operator, goto and Loop along with syntax. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –.
- C has three major decision making instructions—the if statement, the if-else statement, and the switch statement. The if Statement. C uses the keyword if to implement the decision control instruction. The general form of if statement looks like this.
Starting Out with C: From Control Structures through Objects, 7/E.Tony Gaddis.Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming. Ch 01 1.1 Why Program? 1.2 Computer Systems: Hardware and Software 1.3 Programs and Programming Languages 1.4 What Is a Program Made of? 1.5 Input, Processing, and Output 1.6 The Programming Process. Book title: C Programming Book author: Nuha Ali Book subject: C Programming Tutorial Book bookid: 6495407 Book title: Telecom Billing Book author: Zara Ali Book subject: Telecom Billing Tutorial Book bookid: 6495700 Pointers to Structures. You can define pointers to structures in the same way as you define pointer to any other.
C/C++ arrays allow you to define variables that combine several data items of the same kind, but structure is another user defined data type which allows you to combine data items of different kinds.
Structures are used to represent a record, suppose you want to keep track of your books in a library. You might want to track the following attributes about each book −
- Title
- Author
- Subject
- Book ID
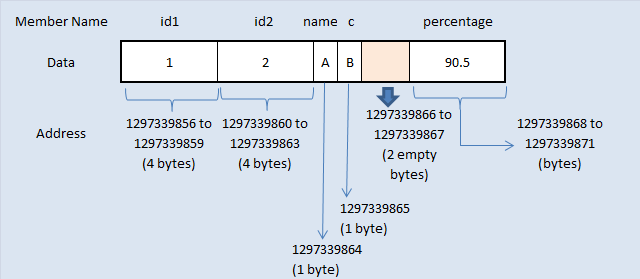
Defining a Structure
To define a structure, you must use the struct statement. The struct statement defines a new data type, with more than one member, for your program. The format of the struct statement is this −
The structure tag is optional and each member definition is a normal variable definition, such as int i; or float f; or any other valid variable definition. At the end of the structure's definition, before the final semicolon, you can specify one or more structure variables but it is optional. Here is the way you would declare the Book structure −
Dynamic Programming Ppt
Accessing Structure Members
To access any member of a structure, we use the member access operator (.). The member access operator is coded as a period between the structure variable name and the structure member that we wish to access. You would use struct keyword to define variables of structure type. Following is the example to explain usage of structure −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Structures as Function Arguments
You can pass a structure as a function argument in very similar way as you pass any other variable or pointer. You would access structure variables in the similar way as you have accessed in the above example −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Pointers to Structures
You can define pointers to structures in very similar way as you define pointer to any other variable as follows −
Now, you can store the address of a structure variable in the above defined pointer variable. To find the address of a structure variable, place the & operator before the structure's name as follows −
To access the members of a structure using a pointer to that structure, you must use the -> operator as follows −
Let us re-write above example using structure pointer, hope this will be easy for you to understand the concept −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
The typedef Keyword

Defining a Structure
To define a structure, you must use the struct statement. The struct statement defines a new data type, with more than one member, for your program. The format of the struct statement is this −
The structure tag is optional and each member definition is a normal variable definition, such as int i; or float f; or any other valid variable definition. At the end of the structure's definition, before the final semicolon, you can specify one or more structure variables but it is optional. Here is the way you would declare the Book structure −
Dynamic Programming Ppt
Accessing Structure Members
To access any member of a structure, we use the member access operator (.). The member access operator is coded as a period between the structure variable name and the structure member that we wish to access. You would use struct keyword to define variables of structure type. Following is the example to explain usage of structure −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Structures as Function Arguments
You can pass a structure as a function argument in very similar way as you pass any other variable or pointer. You would access structure variables in the similar way as you have accessed in the above example −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Pointers to Structures
You can define pointers to structures in very similar way as you define pointer to any other variable as follows −
Now, you can store the address of a structure variable in the above defined pointer variable. To find the address of a structure variable, place the & operator before the structure's name as follows −
To access the members of a structure using a pointer to that structure, you must use the -> operator as follows −
Let us re-write above example using structure pointer, hope this will be easy for you to understand the concept −
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
The typedef Keyword
There is an easier way to define structs or you could 'alias' types you create. Torrent keyscape. For example −
Now, you can use Books directly to define variables of Books type without using struct keyword. Following is the example −
Introduction To Computer Programming Ppt
You can use typedef keyword for non-structs as well as follows −
Control Statements In C Programming Ppt
x, y and z are all pointers to long ints.
